SQL Server Audit Report
Modern SQL Server environments are foundational to enterprise data operations, yet they are also high-value targets for misconfiguration, performance degradation, and security breaches. To ensure these systems are deployed securely and operate reliably from day one, this document defines a structured post-installation audit process aligned with the Microsoft SQL Server Security Best Practices and the CIS Benchmark for SQL Server.
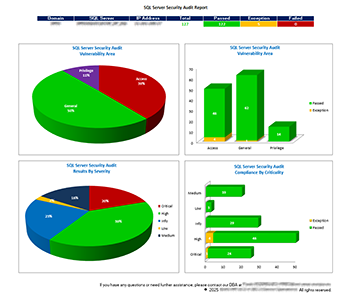
The audit leverages the SQLServer_System_Audit_Report, a curated set of queries and validation procedures, to assess the configuration integrity, security posture, and operational readiness of newly installed SQL Server instances. This process is designed to be executed once, immediately following installation, to establish a hardened and compliant baseline before the system enters production.
This report provides the technical and operational framework for executing a comprehensive SQL Server system audit. It serves as a blueprint for validating that each SQL Server instance is deployed in accordance with enterprise security policies, regulatory requirements, and business continuity objectives.
Beyond identifying misconfigurations or vulnerabilities, the audit process is designed to be:
- Repeatable: Standardized across environments
- Scalable: Adaptable to different deployment sizes and architectures
- Defensible: Aligned with recognized security benchmarks and ready for audit scrutiny
By documenting this process, we ensure that findings are actionable, remediations are traceable, and the methodology is transparent. This guide also acts as a bridge between database administration, infrastructure engineering, and security operations, ensuring that SQL Server environments are not just functional, but resilient and compliant.
Objectives
The primary objectives of this post-installation audit are:
- Security Hardening: Identify and remediate configuration weaknesses that could be exploited by internal or external threats
- Access Control Validation: Ensure authentication mechanisms, role assignments, and privilege boundaries are correctly enforced
- Operational Visibility: Provide insights into how SQL Server is configured, accessed, and monitored to support proactive risk management
- Compliance Assurance: Demonstrate control over sensitive data and system access in support of frameworks like GDPR, ISO 27001, and HIPAA
- Disaster Recovery Readiness: Validate that backup and recovery mechanisms are secure, reliable, and aligned with business SLAs
- Repeatability and Automation: Define a standardized process that can be reused across environments, reducing manual effort and audit fatigue
These objectives ensure that SQL Server environments are secure at deployment and continuously positioned for improvement.
Intended Audience
This document is intended for cross-functional teams responsible for the deployment, validation, and governance of SQL Server infrastructure:
- Database Administrators (DBAs): Execute the audit queries, interpret results, and apply remediations
- Security Operations (SecOps): Validate access controls, monitor for anomalies, and enforce policy compliance
- System Administrators (SysAdmin): Support OS-level configurations, patching schedules, and service account setup
- Compliance Officers and Auditors: Review audit results for alignment with internal controls and external regulations
- Application Owners and Developers: Ensure secure and compliant integration between applications and SQL Server
By aligning these roles around a shared audit framework, the organization promotes accountability, transparency, and operational excellence from the outset.
Systems Implementation [Phases]
|
Phase 1 [Planning & Design]
|
Phase 2 [Infrastructure Preparation]
|
|
Phase 3 [SQL Server Installation]
|
Phase 4 [Post-Configuration Audit & Report]
|
|
Phase 5 [Environment Hardening]
|
Phase 6 [Application Integration & Testing]
|
|
Phase 7 [Go-Live & Operational Readiness]
|
Phase 8 [Documentation & Handover]
|

